Site settings on FastPanel
To open the site settings, first open the Site card and then go to the “Settings” menu.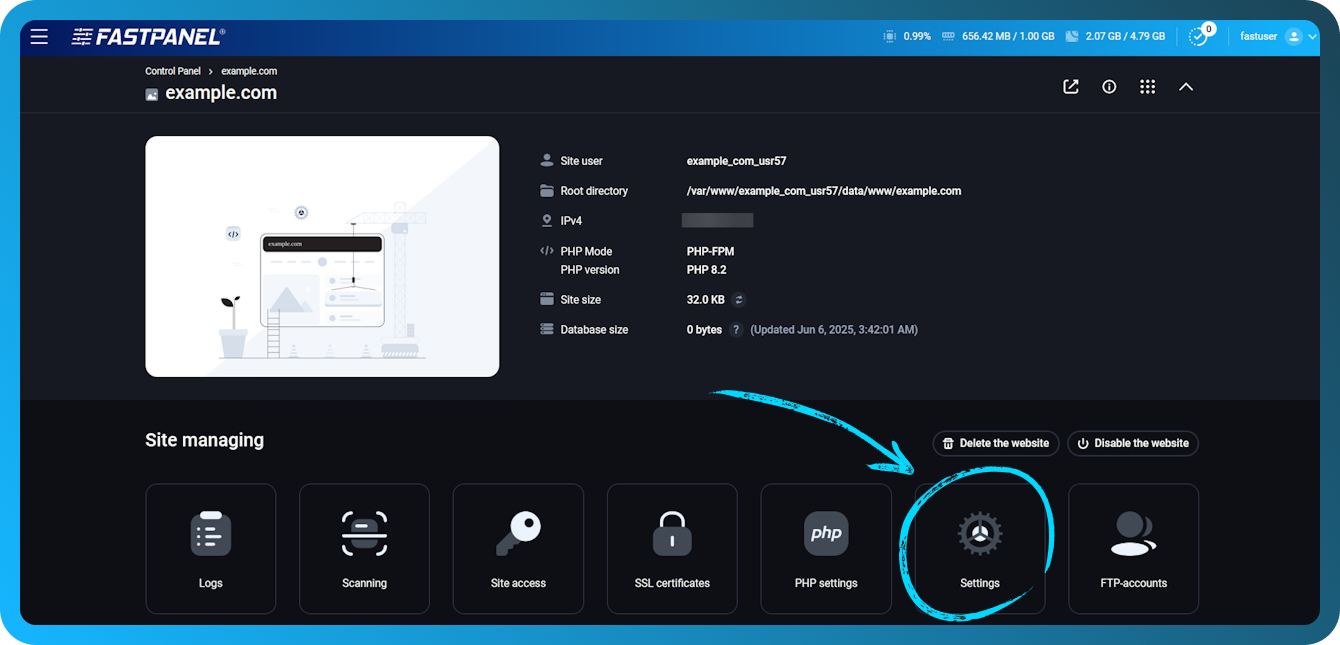
There are several submenus in Settings:
-
Main
-
Static content
-
HTTPS
-
Redirects
-
Log settings
-
Backend (PHP, Upstream, etc.)
In the same menu there is a button “Delete website”, which deletes the site and all data related to it (files, domains, certificates, databases, etc.).
Below is a brief overview of each chapter.
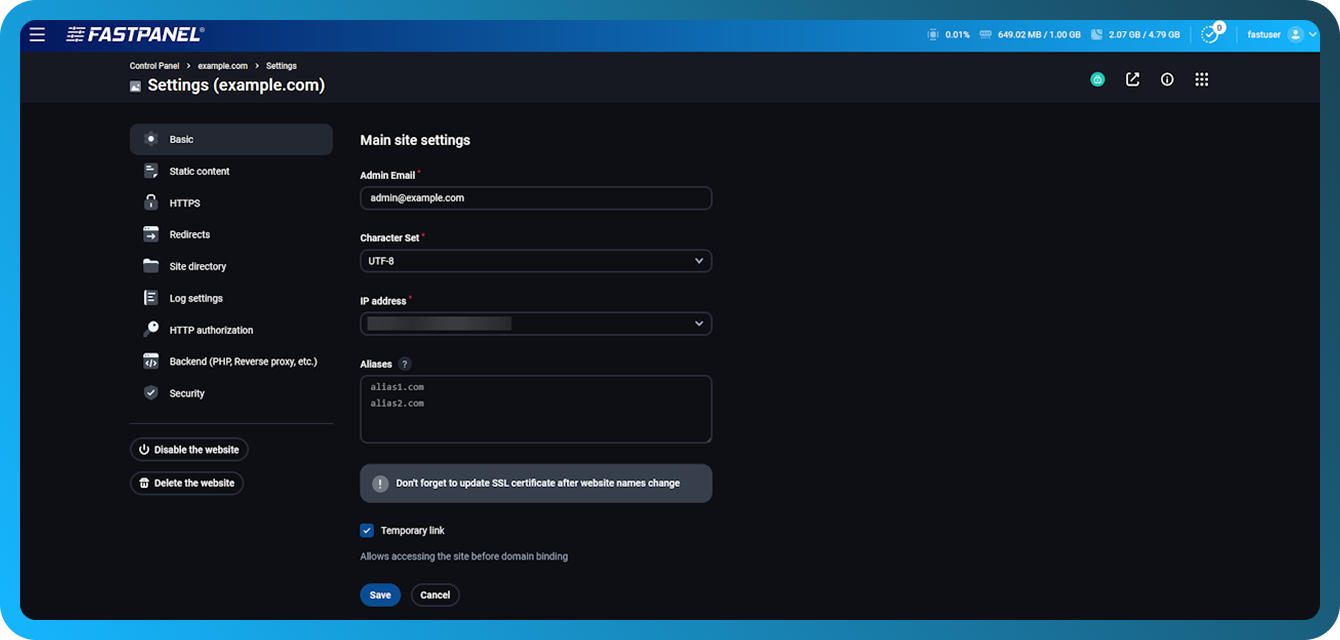
Main settings
This submenu contains basic site parameters:
-
Enable/Disable Site
-
Enable/disable use of temporary link
-
Domain
-
Administrator email
-
Site Coding
-
IP address at which the site will be accessible
-
Site aliases
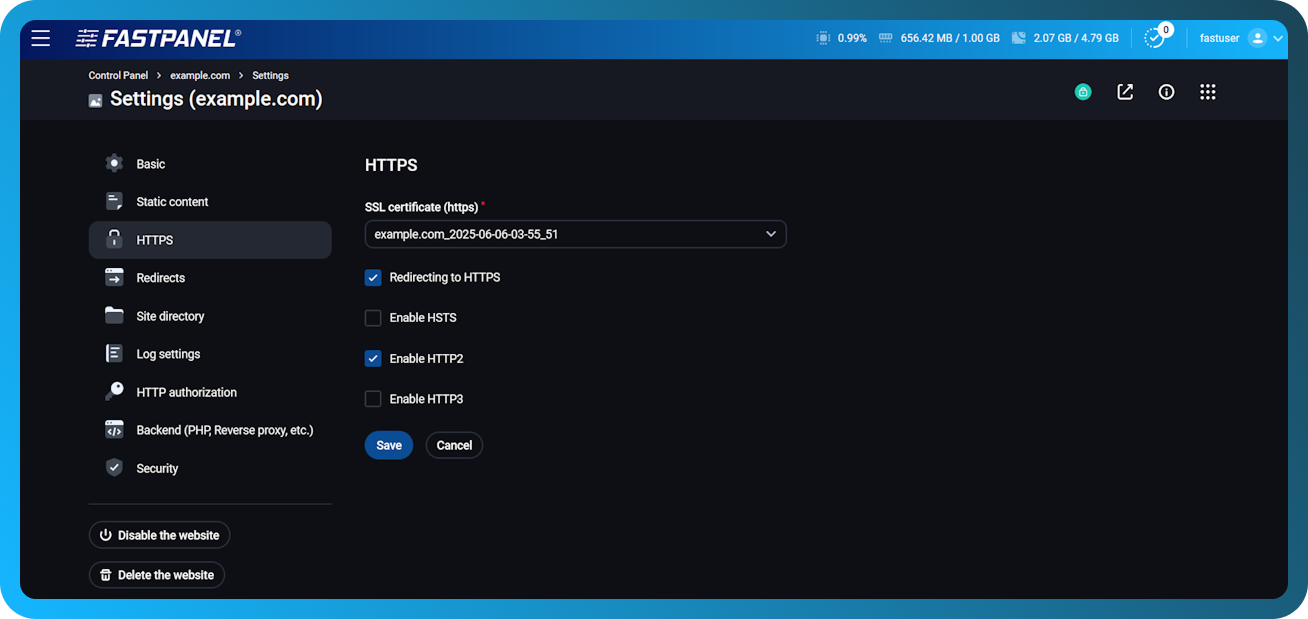
HTTPS
This section contains tools for setting up the site using the HTTPS protocol. After you specify the certificate in the field “SSL certificate”, additional options will appear:
-
HTTPS redirect — redirects all requests to HTTPS with the code 301 (Moved Permanently).
-
HSTS - sends the Strict-Transport-Security header, which forces the browser to use only HTTPS connections.
-
HTTP2 / HTTP3 — enables support for newer versions of the HTTP protocol.
Redirects
In this submenu, redirects for incoming requests to the site are configured:
-
Main site mirror — if enabled, requests from aliases will be redirected to the domain specified in this parameter. For example, here you can configure a redirect from the main domain to www (or vice versa).
-
Enable auto subdomains — automatic subdomains. This option adds a wildcard alias (*.example.com) to the site. Subdomain files will be served from the main domain, but must be placed in folders named after the subdomain in the site's root directory.
For example, for sub0.example.com the root directory would be:/var/www/www-root/data/example.com/sub0
TIP
Please note: wildcard alias (*.example.com) must be added manually in DNS.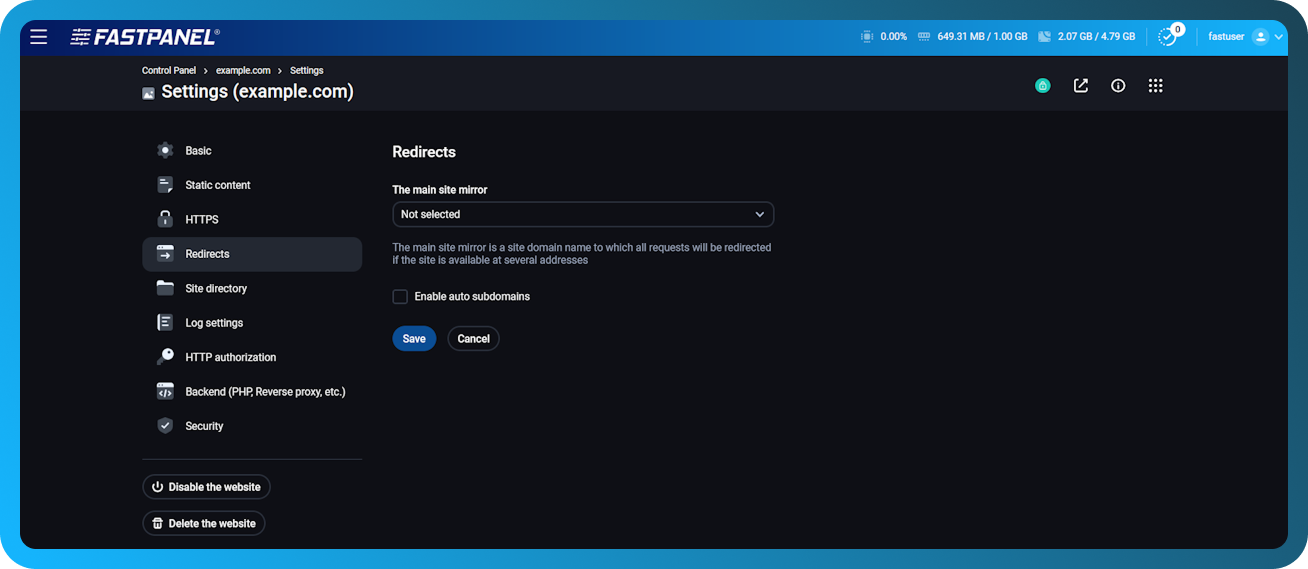
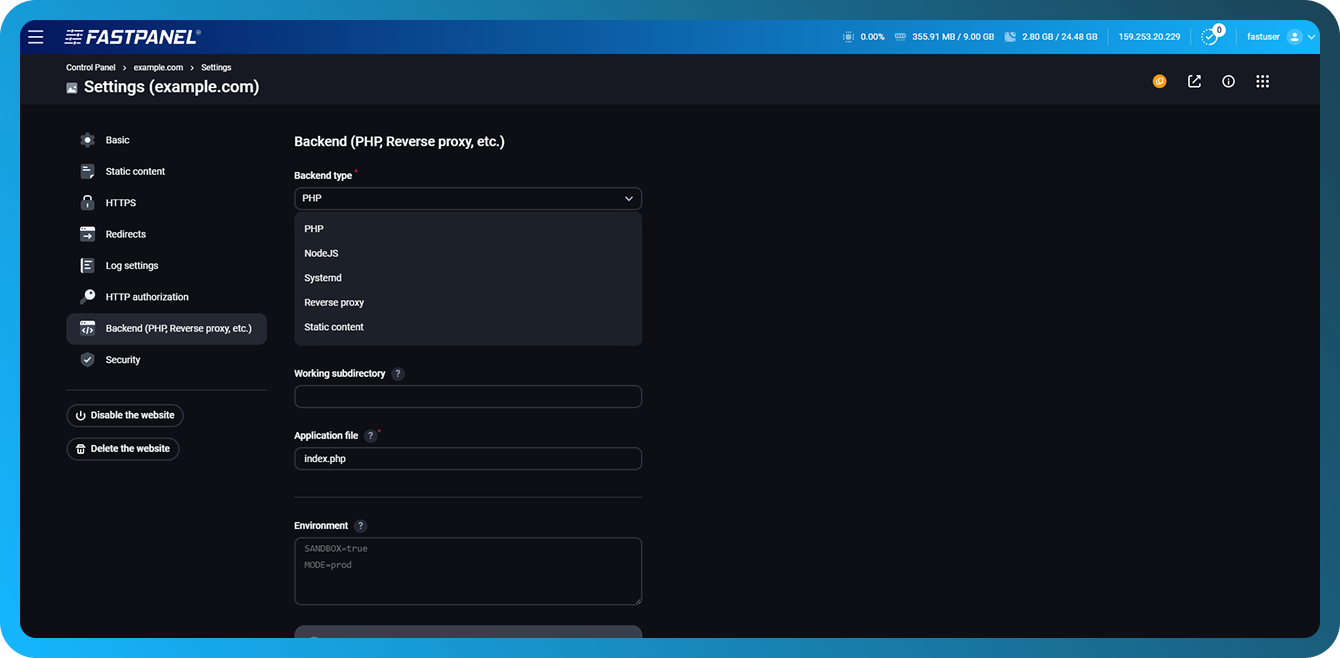
Backend (PHP, Reverse proxy, etc.)
This section is responsible for how the web server processes requests and what backend is used:
-
Backend type — the type of backend that will handle requests. Available variants: PHP, NodeJS, Systemd, Reverse proxy, Static content
-
Handler — a way to connect the backend to a web server, for example Apache module
-
PHP version — PHP version (can be changed only for certain PHP modes)
-
Worker amount — number of workers (relevant only for PHP-FPM mode)
-
Application file — file/page to be displayed when accessing the site
-
Working directory — the root directory of the site (cannot be changed)
-
Working subdirectory — a subdirectory of the site, if it should not work from the root
-
Environment - environment variables passed to the application (for example, operating mode, sandbox settings, etc.)